Die Casting
Chinatech Sourcing Ltd are specialists in the die casting process and work with a number of world class partner organizations in the far east. Some of the benefits of dealing with Chinatech Sourcing Ltd are:
- We can often provide tooling at a fraction of the cost of European sourced parts.
(Typically 50%) - We can often support lower volumes and batch quantities compared to our competitors
- Usually die castings require further post processing including machining and finishing such as powder coating. These additional processes can be expensive, but we can often help you benefit from the lower costs associated with China manufacturing.
- With technical specialists based in the UK and China, we can provide fast and expert feedback on design feasibility and DFM for your components
See our Case Studies page for examples of some of our work.
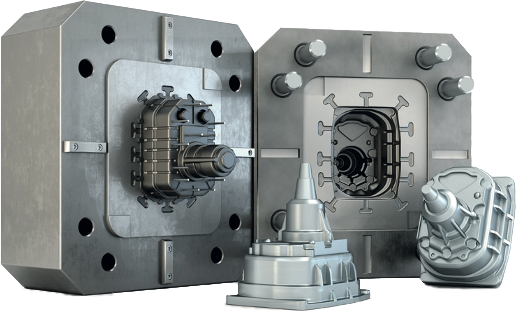
About Die Casting
Die casting is a manufacturing process in which molten metal is poured or forced into steel molds. The molds—also known as tools—are created using steel and are specially designed for each project. This allows each component to be created with accuracy and repeatability. Aluminum, Zinc, and Magnesium are the most commonly used die casting alloys.


Benefits of Die Casting
Die casting can have significant advantages over other manufacturing processes, which often lead to major cost savings, not only in the part price itself but also in the overall cost of production. When you cast a part, you can create complex net shapes, including external threads and complex internal features with minimal draft angles—minimizing secondary operations. You can also combine multiple parts into a single part, eliminating assembly operations and lowering labor costs, with the added benefits of simplified stock control and greater component consistency. Other benefits of die casting include:
- Variable wall thicknesses
- Tighter tolerances
- Fewer steps from raw material to finished part
- Fast production cycle times
- Reduction in material scrap
- Long tool life, especially for zinc and magnesium
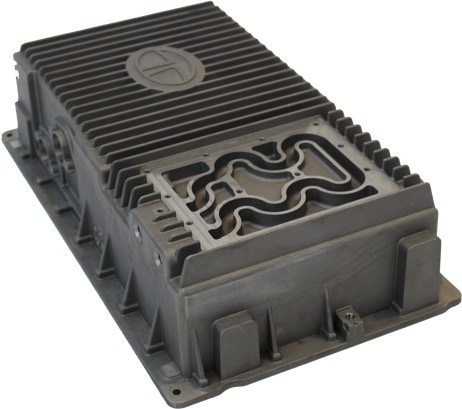


Benefits of Die Casting Alloys
Zinc, aluminum, and magnesium are the three main die casting alloys. They are normally non-ferrous and their mechanical properties vary greatly to fit almost every type of application a manufacturer may need. Not only can die cast alloys withstand high operating temperatures, but they are also fully recyclable. Die cast alloy also have:
- Good corrosion resistance
- High strength and hardness
- High thermal conductivity
- High electrical conductivity
- Outstanding EMI/RFI shielding properties
- Good finishing characteristics

Design for Manufacture (DFM) Points
These are the points we consider when we conduct a DFM on a part designed by a client in order to make improvements:
DRAFT
Draft is a feature added to the part which allows ejection from the mold. Draft is generally a tapered angle between ¼ degree and 1 degree depending upon the size, material, surface finish and process requirements of the part. Adding draft to part allows for easier casting with improved production yields.
RADII & FILLETS
When designing your cast part, ensure there are no sharp corners or edges. All inside corners should have a generous fillet, this increases material flow and improves strength. Adding fillets to inside corners also eliminates potential stress points. Outside corners should have a radius as large as possible as this will help with material flow and part strength.
WALL THICKNESS
The best practice with wall thickness is to be uniform in the design. There is no fixed rule about how thick or thin you can go, the design depends upon your product requirements, however, variation in wall thicknesses creates uneven mold fill and potential turbulent flow in the molten material.
WEIGHT REDUCTION
The target is to reduce weight by optimizing the material volume. The more material used in the part design, the longer the die cavity will take to fill, and the cooling time is extended. Both attributes result in an increase in cost per part. One way to reduce material and weight is to include pockets and hollow sections in the design. These can also help with achieving uniform wall thicknesses throughout the part. If you need to increase the strength and rigidity, you can add ribs.
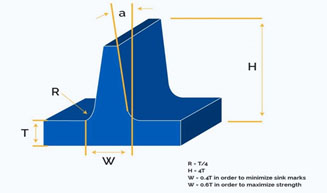
RIBS
Ribs add strength and rigidity to the part; however, the ribs must be designed correctly. Ensure any ribs added have fillets at the corners to eliminate stress concentration points (as per note in radii & fillets above). Ribs should follow this general design rule:
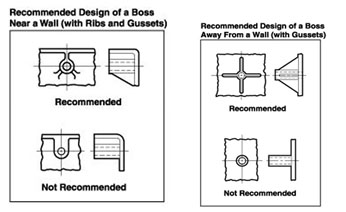
BOSSES
Bosses are added to castings to provide stand-offs and mounting points. The design of bosses should follow the general rules of casting design, uniform wall thickness, fillets and radii and draft angles. The images below show both incorrect boss designs and the correct boss design:
WEIGHT REDUCTION
The target is to reduce weight by optimizing the material volume. The more material used in the part design, the longer the die cavity will take to fill, and the cooling time is extended. Both attributes result in an increase in cost per part. One way to reduce material and weight is to include pockets and hollow sections in the design. These can also help with achieving uniform wall thicknesses throughout the part. If you need to increase the strength and rigidity, you can add ribs.
SHRINKAGE
All metal shrinks during the cooling stage of casting, therefore, the part design needs to have draft applied to the correct surfaces in order to help with the ejection process. The part should always be designed to the desired final dimension as the toolmaker will design the tools to allow for specific material shrinkage.
PARTING LINES
The parting line is where the two halves of the die separate. This needs to be considered during the design stage of the part. It is always best to discuss options with the toolmaker.
